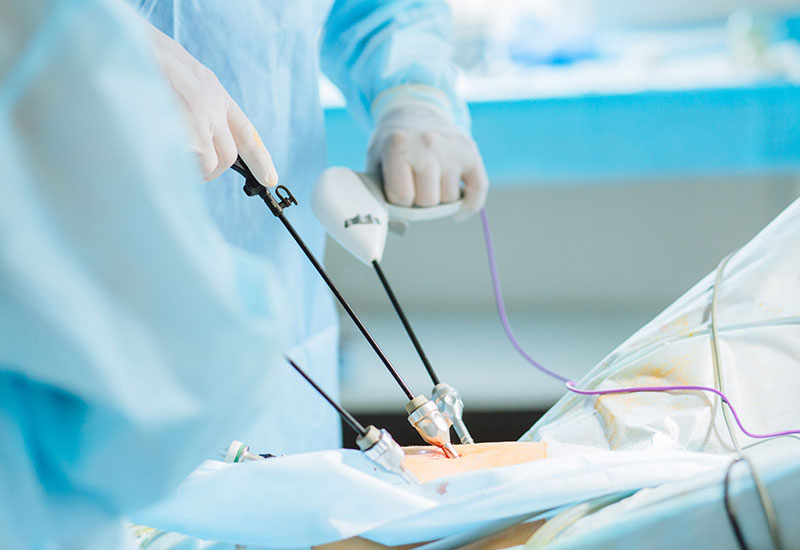
General & Laparoscopic Surgery
General Surgery is a medical specialty that focuses on the diagnosis, treatment, and management of a wide range of surgical conditions, particularly those related to the abdominal organs, soft tissues, and some areas of the head and neck. General surgeons are trained to perform a variety of surgeries to treat both common and complex conditions, and they often work in collaboration with other specialists, depending on the complexity of the disease.
Key areas of general surgery include:
-
Gastrointestinal (GI) Surgery: Surgery related to the digestive system, including:
- Appendectomy: Removal of the appendix in cases of appendicitis.
- Cholecystectomy: Removal of the gallbladder, often due to gallstones or inflammation.
- Bowel Resection: Removal of parts of the intestine to treat conditions like cancer, diverticulitis, or inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
- Colostomy: Surgical creation of an opening in the colon for waste to leave the body.
-
Hernia Surgery: General surgeons treat various types of hernias, including:
- Inguinal Hernia: A protrusion of abdominal contents through the inguinal canal.
- Umbilical Hernia: A bulge near the belly button.
- Hiatal Hernia: A condition where part of the stomach pushes up through the diaphragm into the chest.
-
Breast Surgery: General surgeons perform procedures for conditions like breast cancer, including:
- Mastectomy: Removal of the breast tissue to treat breast cancer.
- Lumpectomy: Removal of a breast lump or tumor while preserving most of the breast tissue.
-
Endocrine Surgery: Surgical treatment of the endocrine glands, such as:
- Thyroidectomy: Removal of part or all of the thyroid gland, often due to cancer or hyperthyroidism.
- Parathyroid Surgery: Treatment of parathyroid disorders that cause abnormal calcium levels.
-
Trauma Surgery: Surgical intervention for injuries due to accidents, falls, or violence. This includes:
- Repair of internal bleeding, organ injuries, and fractures.
-
Skin and Soft Tissue Surgery: Removal of cysts, lipomas, abscesses, or skin cancers.
-
Oncologic Surgery: Surgical treatment of various cancers, including the removal of tumors and affected tissues.
General surgeons can treat both emergency and elective surgical conditions. They are trained to manage pre-operative, operative, and post-operative care, ensuring that patients recover effectively from their surgeries.
Laparoscopic Surgery (Minimally Invasive Surgery)
Laparoscopic surgery, also known as minimally invasive surgery (MIS) or keyhole surgery, is a technique used in general surgery and other specialties that allows surgeons to perform procedures through small incisions (usually less than 1 cm in size), with the assistance of a laparoscope. A laparoscope is a long, thin instrument with a light and camera at the end, which allows the surgeon to view the internal structures of the body on a monitor. Specialized tools are inserted through small incisions to perform the surgery.
Laparoscopic surgery has become popular due to its many advantages over traditional open surgery, including:
- Smaller Incisions: The small incisions result in less trauma to the body, leading to reduced risk of infection and less scarring.
- Reduced Pain: The smaller incisions typically lead to less post-operative pain, allowing for quicker recovery.
- Shorter Hospital Stays: Because of the less invasive nature of the procedure, patients often experience shorter hospital stays and quicker return to daily activities.
- Quicker Recovery: Overall recovery time is often faster than traditional surgery, with many patients able to resume normal activities sooner.
- Less Blood Loss: Minimally invasive techniques tend to result in less blood loss during surgery.
Common Types of Laparoscopic Surgery
-
Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy (Gallbladder Removal): This is one of the most common laparoscopic surgeries, performed to remove the gallbladder due to gallstones or gallbladder disease.
-
Laparoscopic Appendectomy (Appendix Removal): The appendix is removed through small incisions, typically in cases of appendicitis.
-
Laparoscopic Hernia Repair: Used to treat inguinal, umbilical, and other types of hernias, where the surgeon repairs the hernia through small incisions using special instruments.
-
Laparoscopic Bowel Resection: In cases of bowel disease or cancer, a portion of the intestine may be removed through minimally invasive surgery.
-
Laparoscopic Gastric Bypass (Bariatric Surgery): For weight loss, a surgeon may use laparoscopic techniques to create a smaller stomach pouch or bypass part of the small intestine.
-
Laparoscopic Ovarian Cystectomy: In gynecological surgery, laparoscopic techniques are used to remove ovarian cysts, often with quicker recovery times compared to traditional open surgery.
-
Laparoscopic Nissen Fundoplication: This is a surgery to treat severe gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) by wrapping the top of the stomach around the lower esophagus to prevent acid reflux.
-
Laparoscopic Colectomy: The removal of part or all of the colon, often done to treat colon cancer or inflammatory bowel disease.
