Orthopaedic/Orthoscopic Surgery and Joint Replacement
Orthopaedic surgery is a medical specialty focused on diagnosing, treating, rehabilitating, and preventing musculoskeletal disorders. These disorders involve the bones, joints, muscles, ligaments, tendons, and nerves. Orthopaedic surgeons treat conditions related to trauma, sports injuries, degenerative diseases, infections, congenital disorders, and tumors affecting the musculoskeletal system.
Orthopaedic surgeries can be broadly categorized into:
- Trauma Surgery: Treatment of fractures, dislocations, and soft tissue injuries.
- Joint Replacement: Replacing a damaged joint with a prosthesis, often done for hip, knee, and shoulder joints.
- Spinal Surgery: Correcting issues such as herniated discs, spinal stenosis, and scoliosis.
- Arthroscopy: Minimally invasive surgery to diagnose and treat joint problems (e.g., cartilage damage).
- Sports Medicine: Treatment of injuries related to physical activity or athletic performance.
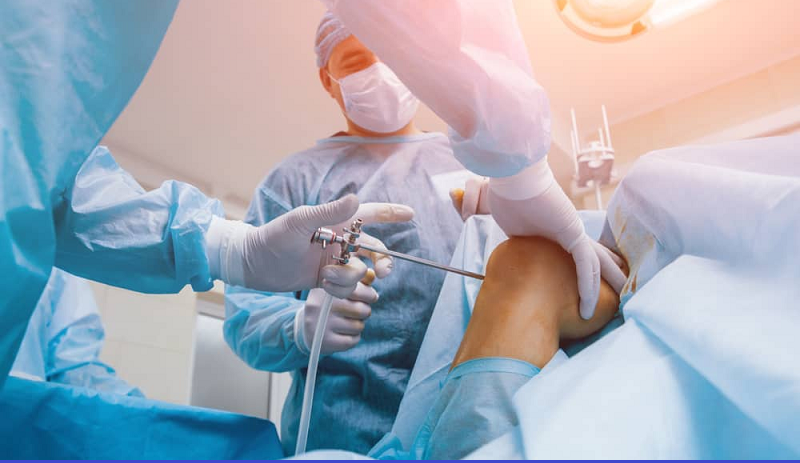
Arthroscopic Surgery
Arthroscopic surgery is a minimally invasive technique used to diagnose and treat joint problems. An orthopaedic surgeon inserts a small camera, called an arthroscope, into the joint through tiny incisions. This camera allows the surgeon to view the inside of the joint on a monitor, and specialized instruments are used to treat the condition.
Common arthroscopic surgeries include:
- Knee Arthroscopy: For treating tears in the meniscus, cartilage damage, or ligament issues.
- Shoulder Arthroscopy: For repairing rotator cuff tears, shoulder instability, or impingement.
- Ankle Arthroscopy: To address cartilage damage, ligament tears, or other joint issues.
Arthroscopy generally offers faster recovery times and fewer complications compared to traditional open surgery.
Joint Replacement Surgery
Joint replacement, or arthroplasty, involves replacing a damaged joint with an artificial one (prosthesis). It is commonly performed when conservative treatments like medication, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes no longer relieve pain or improve function. The most common joint replacements are:
- Hip Replacement: This procedure replaces a worn-out or damaged hip joint, often due to arthritis or fractures, with a prosthetic hip joint.
- Knee Replacement: For severe arthritis or knee injuries, the damaged portions of the knee joint are replaced with metal and plastic components.
- Shoulder Replacement: Replacing the shoulder joint to relieve pain and improve function, often due to arthritis or rotator cuff tears.
- Elbow Replacement: Used when arthritis or fractures damage the elbow joint, often improving mobility and reducing pain.
